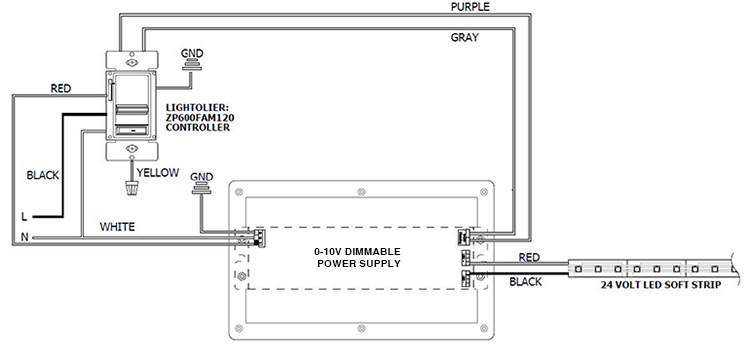
Introduction to forward phase dimming
Dimming lights is a common and convenient way to adjust the brightness of a room or space to suit different activities or moods. It can also help save energy by reducing the amount of electricity needed to power the light. There are various methods for dimming lights, and one of them is called forward phase dimming.
But what exactly is forward phase dimming, and how does it work? In this article, we will explore the basics of forward phase dimming and discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
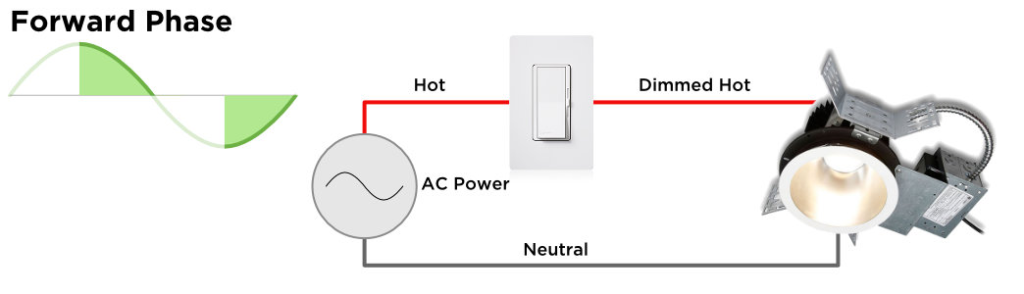
Before diving into the details, let’s define what forward phase dimming is. In simple terms, it is a method of dimming lights by manipulating the phase of the electrical current that powers them. AC (alternating current) electrical current is constantly changing direction and is used to power most household and commercial lighting. By adjusting the phase of the current, the brightness of the light can be controlled.
Forward phase dimming is a popular choice for lighting control due to its compatibility with a wide range of light sources and its smooth dimming performance. However, like any other dimming method, it also has its own set of limitations and potential drawbacks.
In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of forward phase dimming and examine its pros and cons in more depth. We will also consider the factors to consider when deciding on a dimming method for a lighting system. By the end of this article, you should have a good understanding of what forward phase dimming is and whether it is the right choice for your needs.
How Forward Phase Dimming Works
To understand how forward phase dimming works, it is helpful to first have a basic understanding of AC electrical current and phase.
AC electrical current is an alternating current that changes direction periodically. It is the type of current that powers most household and commercial lighting. The voltage of AC electrical current also changes over time, following a sine wave pattern. The period of one complete cycle of the sine wave is called a “phase.”
In forward phase dimming, the phase of the electrical current is adjusted to control the brightness of the light. Specifically, the dimmer reduces the amount of time that the current flows to the light, which reduces the overall amount of power delivered to the light. As a result, the light becomes dimmer.
This dimming method is called “forward phase” because the phase angle of the current is advanced or “shifted forward” relative to the voltage. This shift causes the current to be out of phase with the voltage, which reduces the power delivered to the light.
Forward phase dimming is often accomplished using a device called a “triac,” which is a type of electronic switch that can control the flow of AC electrical current. The triac is controlled by a dimmer switch or a remote control, allowing the user to adjust the brightness of the light.
One of the key advantages of forward phase dimming is its compatibility with a wide range of light sources, including incandescent, halogen, and many types of LED lights. It is also known for providing smooth dimming performance, with minimal flicker or buzz.
However, it is important to note that forward phase dimming may not work with all types of light sources and may have a limited dimming range for some light sources.
Advantages of Forward Phase Dimming
Forward phase dimming has several advantages that make it a popular choice for lighting control. Here are some of the key benefits of using this dimming method:
- Energy efficiency: Dimming lights can save energy by reducing the amount of electricity needed to power the light. This can be especially useful in spaces that are only partially occupied or that require different levels of lighting at different times of day. By using forward phase dimming, you can easily adjust the brightness of the light to match the needs of the space and save energy in the process.
- Compatibility with a wide range of light sources: Forward phase dimming is compatible with many types of light sources, including incandescent, halogen, and many types of LED lights. This makes it a versatile option for lighting control in a variety of settings.
- Smooth dimming performance: Forward phase dimming is known for providing smooth dimming performance, with minimal flicker or buzz. This can be especially important in spaces where the lighting needs to be carefully controlled, such as in theaters or galleries.
- Easy installation: Forward phase dimming systems are typically easy to install and can be used with a variety of dimmer switches or remote controls. This makes them a convenient and user-friendly option for lighting control.
In summary, forward phase dimming offers a range of advantages, including energy efficiency, compatibility with a wide range of light sources, smooth dimming performance, and easy installation. These benefits make it a popular choice for lighting control in many different types of settings.
Disadvantages of Forward Phase Dimming
While forward phase dimming has many advantages, it is important to also consider its potential drawbacks. Here are some of the key disadvantages of using this dimming method:
- Limited dimming range for some light sources: One potential limitation of forward phase dimming is that it may not work with all types of light sources, or it may have a limited dimming range for some light sources. For example, some LED lights may not dim as low as desired with forward phase dimming, or they may exhibit flicker or color shift at low brightness levels. It is important to carefully consider the specific characteristics of the light source when choosing a dimming method.
- Potential for interference with other electronic devices: Another potential drawback of forward phase dimming is that it can interfere with other electronic devices, such as motor-driven appliances or devices with power supplies that are sensitive to phase changes. This can be caused by the phase shift that occurs during dimming, which can affect the operation of other electronic devices.
- Higher cost: In some cases, forward phase dimming systems may be more expensive than other dimming methods, such as leading edge dimming or trailing edge dimming. This can be a factor to consider when budgeting for a lighting control system.
In summary, forward phase dimming may have limitations when used with certain light sources and may interfere with other electronic devices. It may also be more expensive than some other dimming methods. These potential drawbacks should be carefully considered when deciding on a dimming method for a lighting system.
Conclusion: Understanding the Pros and Cons of Forward Phase Dimming for Lighting Control

In this article, we have explored the basics of forward phase dimming and examined its advantages and disadvantages. We have learned that forward phase dimming is a method of dimming lights by adjusting the phase of the electrical current that powers them. It is compatible with many types of light sources and provides smooth dimming performance, but it may have limitations and potential interference issues.
When deciding on a dimming method for a lighting system, it is important to consider the specific needs and preferences of the space. Factors such as the type of light source, the desired dimming range, and the potential for interference with other electronic devices should all be taken into account.
In summary, forward phase dimming is a widely used method for dimming lights that offers a range of advantages, but it is not without its own set of limitations and potential drawbacks. By understanding the basics of forward phase dimming, you can make an informed decision about the best dimming method for your lighting system.
FAQs about forward phase dimming
Forward phase dimming is a method of dimming lights by adjusting the phase of the electrical current that powers them. It is a popular choice for lighting control due to its compatibility with a wide range of light sources and its smooth dimming performance.
Forward phase dimming works by reducing the amount of time that the electrical current flows to the light, which reduces the overall amount of power delivered to the light. This is typically accomplished using a device called a “triac,” which is a type of electronic switch that can control the flow of AC electrical current. The triac is controlled by a dimmer switch or a remote control, allowing the user to adjust the brightness of the light.
Forward phase dimming has several advantages, including energy efficiency, compatibility with a wide range of light sources, smooth dimming performance, and easy installation.
Some of the potential disadvantages of forward phase dimming include a limited dimming range for some light sources, the potential for interference with other electronic devices, and higher cost in some cases.
Forward phase dimming is compatible with many types of light sources, including incandescent, halogen, and many types of LED lights. However, it may not work with all types of light sources or may have a limited dimming range for some light sources. It is important to carefully consider the specific characteristics of the light source when choosing a dimming method.