- Introduction to Overpowered PSUs
- The Basics of PSUs
- The Dangers of an Overpowered PSU
- Choosing the Right PSU for Your System
- Conclusion: The Importance of Choosing the Right PSU for Your Computer System
- FAQs about Overpowered PSUs
- Introduction to Overpowered PSUs
- The Basics of PSUs
- The Dangers of an Overpowered PSU
- Choosing the Right PSU for Your System
- Conclusion: The Importance of Choosing the Right PSU for Your Computer System
- FAQs about Overpowered PSUs
Introduction to Overpowered PSUs
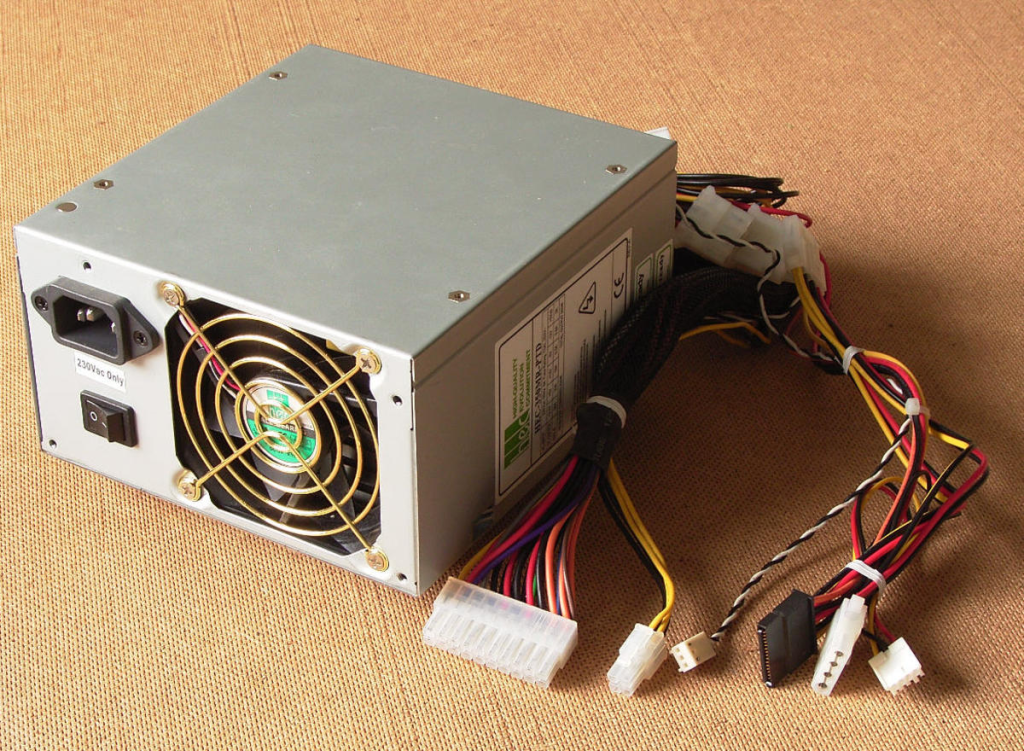
When building or upgrading a computer, choosing the right power supply unit (PSU) is important. The PSU is responsible for converting AC power from a wall outlet into DC power that the computer’s components can use, and it is an essential component that must be selected carefully. It is important to choose a PSU that is powerful enough to meet the needs of the computer’s components, but is it possible to have a PSU that is too powerful? In this article, we will explore the potential dangers and consequences of using an overpowered PSU and offer tips on choosing the right PSU for your computer system.
So, how do you choose the right PSU for your computer system? The first step is to determine the power requirements of your computer’s components. This will help you determine the minimum wattage needed for your PSU. Once you have a rough estimate of the power requirements of your system, you can select a PSU that meets or exceeds these requirements.
By choosing the right PSU for your computer, you can ensure that your system gets the p
ower it needs while minimizing the risks of damage and wasted energy.
The Basics of PSUs
Now that we understand the potential dangers of using an overpowered PSU let’s delve deeper into the basics of power supply units. As mentioned in the introduction, a PSU is a device that supplies power to a computer and its components. It converts AC power from a wall outlet into DC power, which the computer’s components need to function. The wattage of a PSU is an important factor to consider when selecting a PSU, as it determines the amount of power that the PSU can provide. Generally, a higher-wattage PSU can supply more power to the computer, but this does not necessarily mean that it is the best choice for every system.
Factors to consider when selecting a PSU
Efficiency ratings
In addition to wattage, there are other important factors to consider when selecting a PSU. Efficiency ratings, such as 80 Plus, measure the efficiency of a PSU and can affect the amount of electricity it consumes and the amount of heat it generates. The higher the efficiency rating, the more efficient the PSU is at converting AC power into DC power and the less heat it will generate. This can be important for computers used in a hot or humid environment, as excess heat can damage components and shorten the computer’s lifespan.
Form factor
The form factor is another important factor to consider when selecting a PSU. The form factor refers to the size and shape of the PSU and determines whether it will fit in the computer case. Several common form factors exist for PSUs, including ATX, SFX, and microATX. Choosing a PSU with a form factor compatible with your computer case is important, as using a PSU with the wrong form factor can lead to installation problems and potentially damage the computer.
Price
Price is another factor to consider when selecting a PSU. Higher-quality PSUs are more expensive but tend to be more reliable and have longer lifespans. It is important to strike a balance between price and quality when selecting a PSU, as purchasing a cheap, low-quality PSU can lead to problems down the line.
In summary, when selecting a PSU for a computer system, it is important to consider the wattage, efficiency ratings, form factor, and price. By considering these factors, you can choose a PSU that meets the power requirements of your system and is compatible with your computer case. You can also ensure that you get a reliable and long-lasting PSU that will provide reliable power to your computer for years to come.
The Dangers of an Overpowered PSU

We’ve established that a PSU can be too powerful for a computer system, but what are the dangers and consequences of using an overpowered PSU?
Wasted energy and increased electricity
Using a PSU that is too powerful for a computer system can lead to wasted energy and increased electricity bills. When a PSU provides more power than the computer’s components need, the excess power is simply wasted and contributes to higher electricity bills. In addition to the financial costs, this also has an environmental impact as it results in increased carbon emissions from the production and distribution of electricity.
Increased heat generation
Using an overpowered PSU can also lead to increased heat generation, which can be a problem for computers in a hot or humid environment. Excess heat can damage components and shorten the lifespan of the computer. It can also lead to decreased performance, as components may become sluggish or fail to function properly due to the increased heat.
Risk to the computer
In addition to the risks of wasted energy and increased heat generation, using an overpowered PSU can also pose a risk to the computer. An overpowered PSU can potentially damage components due to the excess power being supplied to the system. This can lead to expensive repairs or even replacing the entire computer.
In summary, the dangers of using an overpowered PSU include wasted energy, increased electricity bills, heat generation, and potential damage to the computer’s components. It is important to choose a PSU that is powerful enough to meet the needs of the computer’s components but not so powerful that it is providing more power than the system needs. Choosing the right PSU for your computer can minimize the risks of wasted energy, increased heat generation, and component damage.
Choosing the Right PSU for Your System
Now that we’ve discussed the potential dangers of using an overpowered PSU, let’s examine the steps you can take to choose the right PSU for your computer system.
The first step is to determine the power requirements of your computer’s components. This will help you determine the minimum wattage needed for your PSU. It is important to consider the power requirements of all components, including the processor, graphics card, motherboard, and any additional peripherals or components.
There are several tools available that can help you determine the power requirements of your computer’s components. One option is to use a power supply calculator, which allows you to input your components’ specifications and estimate your system’s power requirements. You can also consult the documentation for your components, as many manufacturers will list the power requirements in the specifications.
Once you have a rough estimate of the power requirements of your system, you can select a PSU that meets or exceeds these requirements. It is generally recommended to choose a PSU with a wattage at least 50-100 watts higher than the estimated power requirements of your system to allow for future upgrades or to account for any overestimations in the power requirements.
In addition to wattage, it is important to consider efficiency ratings, form factors, and price when selecting a PSU. Efficiency ratings, such as 80 Plus, measure the efficiency of a PSU and can affect the amount of electricity it consumes and the amount of heat it generates. The form factor determines the size and shape of the PSU and whether it will fit in the computer case. Price is also an important factor to consider, as higher-quality PSUs tend to be more expensive and more reliable and have longer lifespans.
It is also important to consider the reputation and reliability of the PSU brand when selecting a PSU. Look for brands with a good track record of producing high-quality, reliable PSUs. You can do this by reading reviews, consulting online forums, and seeking recommendations from trusted sources.
Conclusion: The Importance of Choosing the Right PSU for Your Computer System
In conclusion, choosing the right power supply unit (PSU) for your computer system ensures that it gets the power it needs to function properly and efficiently. An overpowered PSU can lead to wasted energy, increased electricity bills, heat generation, and potential damage to the computer’s components. On the other hand, a PSU that is not powerful enough can lead to an insufficient power supply, resulting in decreased performance or even component failure.
To choose the right PSU for your system, it is important to determine the power requirements of your computer’s components and select a PSU that meets or exceeds these requirements. Consider factors such as wattage, efficiency ratings, form factor, and price when selecting a PSU, and look for reputable and reliable brands. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your computer is getting the power it needs while minimizing the risks of wasted energy, increased heat generation, and component damage.
FAQs about Overpowered PSUs
A PSU (Power Supply Unit) is a device that supplies power to a computer and its components. It converts AC power from a wall outlet into DC power, which the computer’s components need to function. The wattage of a PSU determines the amount of power it can provide to the computer.
A PSU can be too powerful for a computer system. Using a PSU that is too powerful can lead to wasted energy, increased electricity bills, increased heat generation, and potential damage to the computer’s components. It is important to choose a PSU that is powerful enough to meet the needs of the computer’s components but not so powerful that it is providing more power than the system needs.
There are several tools available that can help you determine the power requirements of your computer’s components. One option is to use a power supply calculator, which allows you to input your components’ specifications and estimate your system’s power requirements. You can also consult the documentation for your components, as many manufacturers will list the power requirements in the specifications.
When selecting a PSU, it is important to consider the wattage, efficiency ratings, form factor, and price. The wattage determines the power the PSU can provide to the computer. Efficiency ratings, such as 80 Plus, measure the efficiency of a PSU and can affect the amount of electricity it consumes and the amount of heat it generates. The form factor determines the size and shape of the PSU and whether it will fit in the computer case. Price is also an important factor to consider, as higher-quality PSUs tend to be more expensive and more reliable and have longer lifespans.